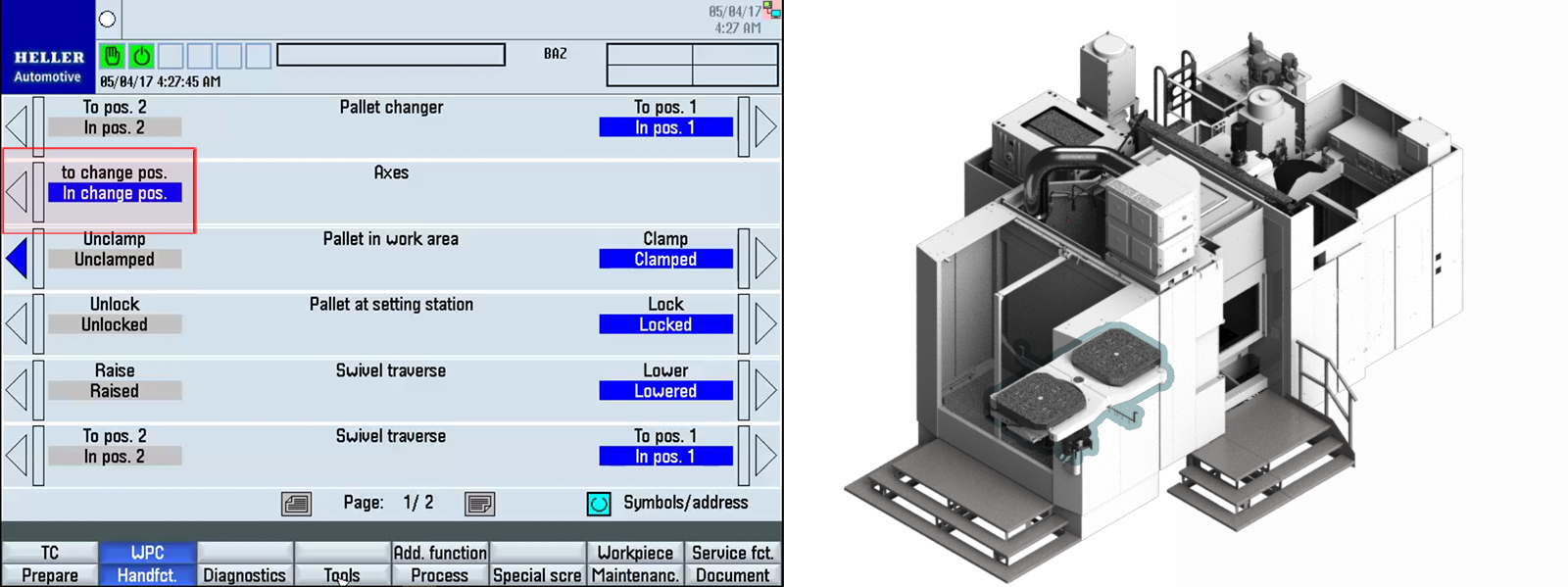
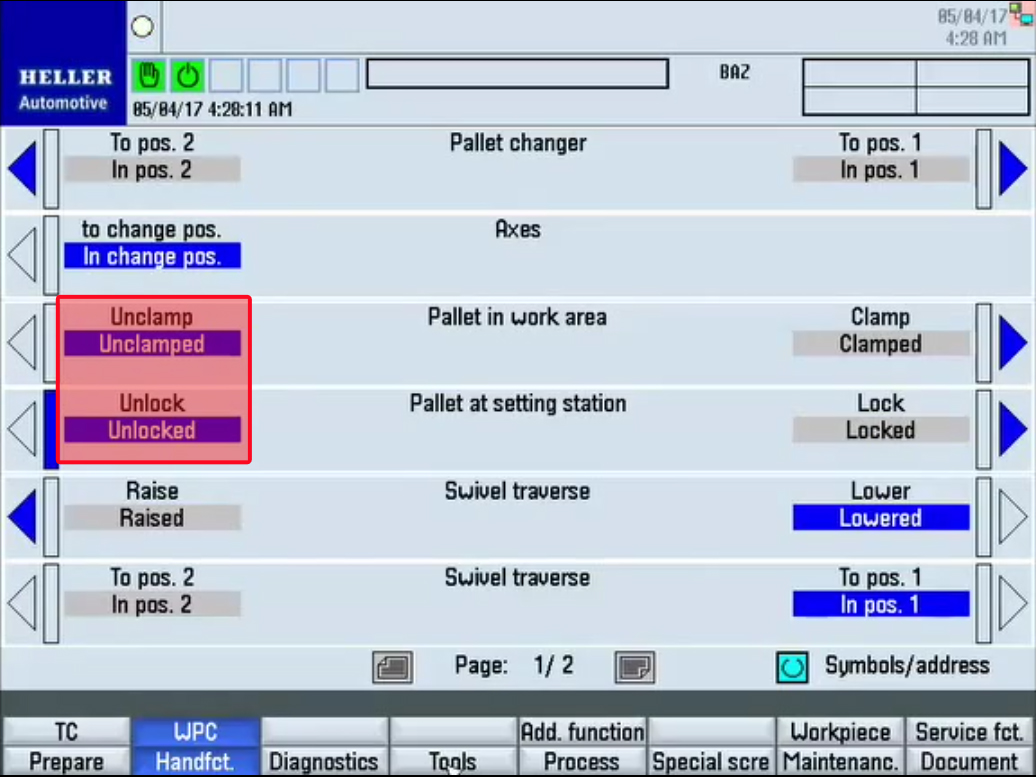
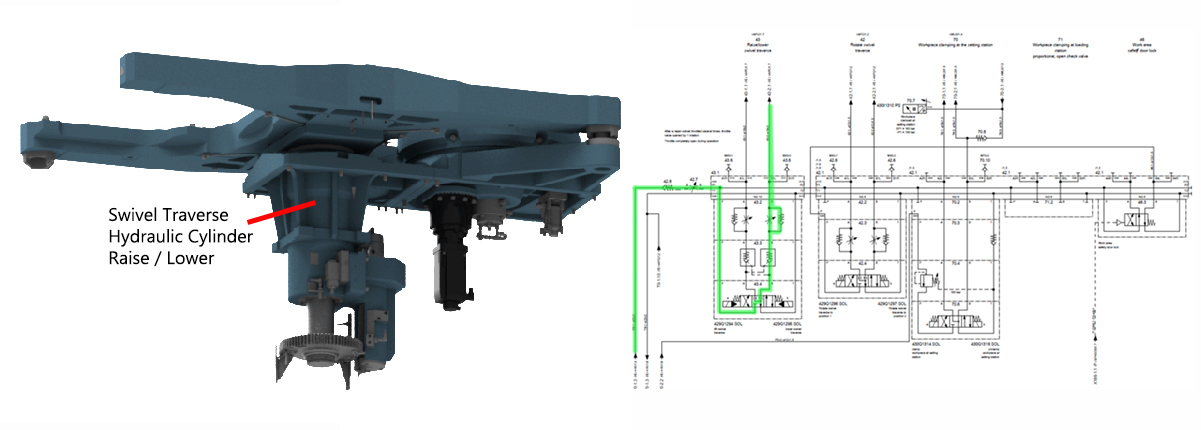
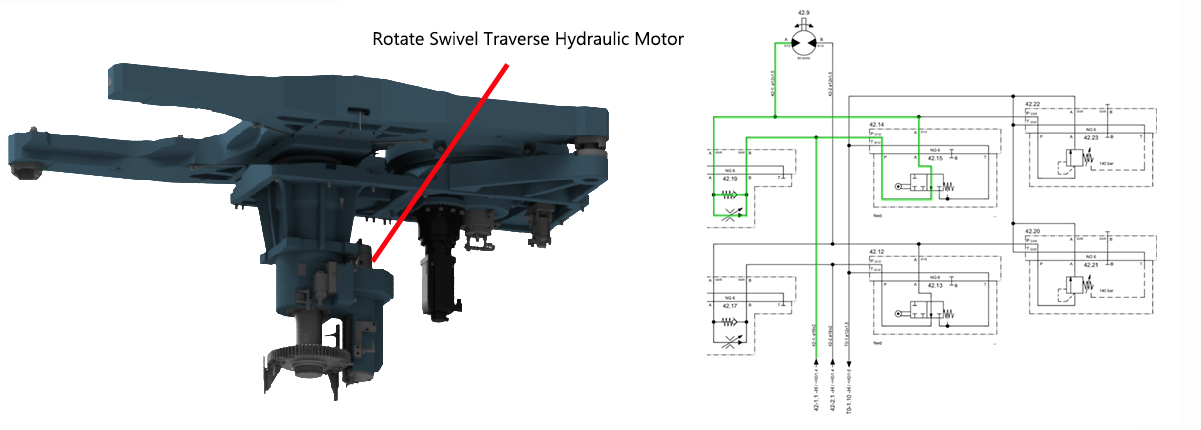
Function of Pallet Changer
Reference Files
Tools Required
Torque Chart
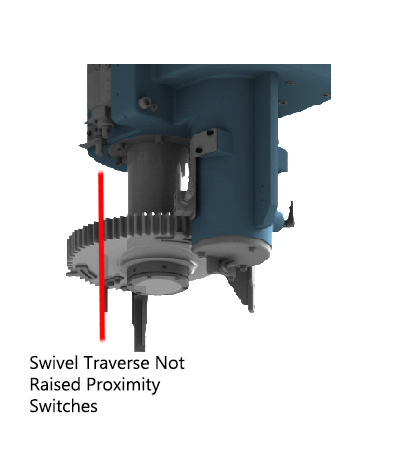
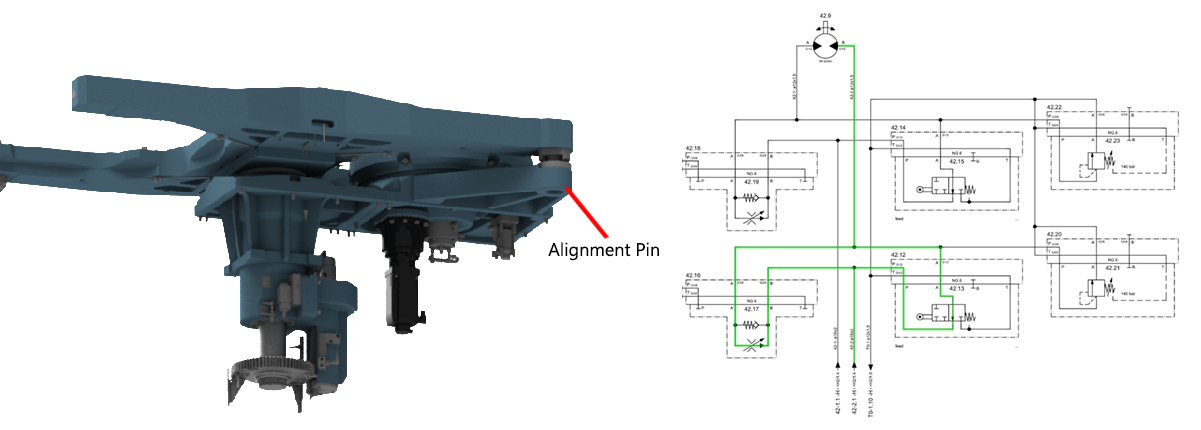
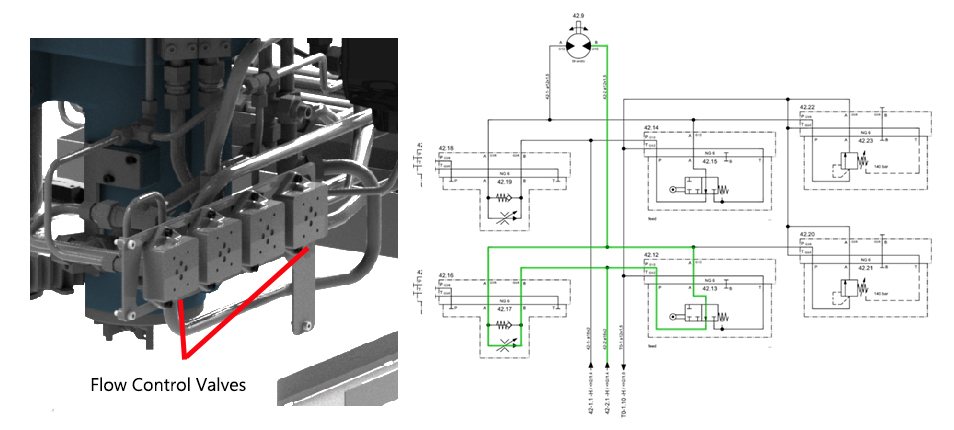
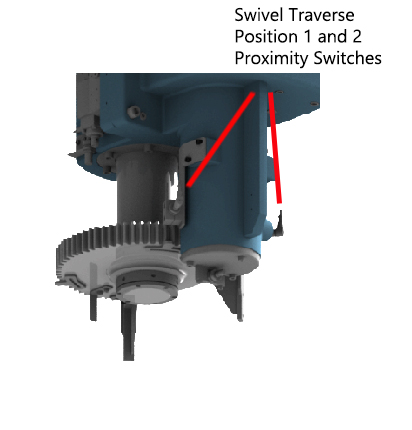
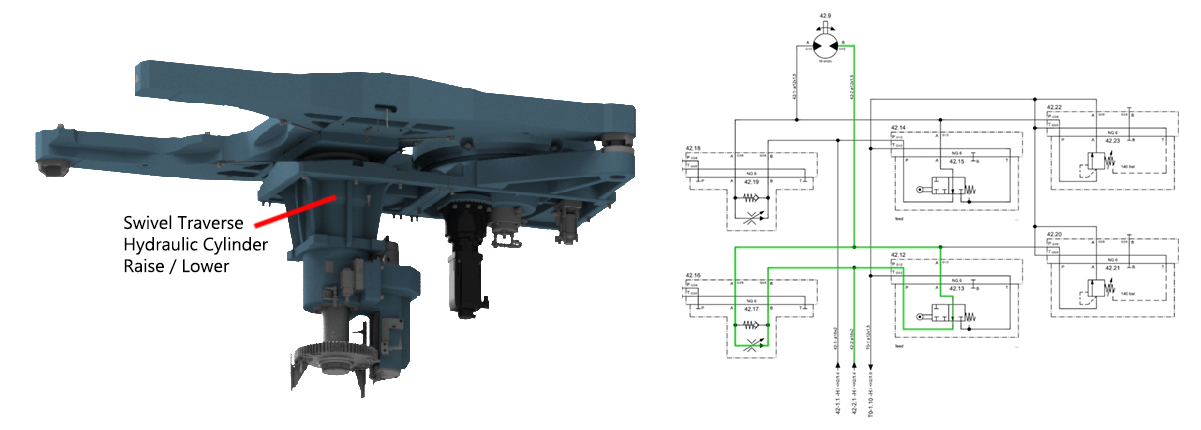
Step 1:Step 2:Step 3:Fluid is supplied to the raise side of swivel traverse raise lower hydraulic cylinder which in turn raises the pallets. Step 4:Step 5:Step 6:The speed is reduced approximately 100.00 mm away from the alignment pin, when the directional control valve (rollers) are actuated (closed) by the cam lobe ramps. Step 7:When the directional control valve (rollers) are actuated (closed), all return line fluid is then diverted through the appropriate flow control valve which reduces the pallet changer rotational speed. Step 8:Step 9:Fluid is supplied to the lower side of the swivel traverse raise lower hydraulic cylinder which in turn lowers the pallets. Step 10:Step 11: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||